第39回信号処理シンポジウム参加報告
2024年12月16日 (月) ~ 18日 (水) にかけて北海道大学にて第39回信号処理シンポジウムが開催されました.
本研究室からは以下の発表を行いました.
〇藤崎達也1,村松正吾1 (1. 新潟大学),”Unrolled Fast Griffin-Lim アルゴリズムによるパラメータ系列推定”
〇伊藤隆人1,内藤翼1,安田浩保1,永原正章2,田中雄一3,村松正吾1 (1. 新潟大学,2. 広島大学,3. 大阪大学),”有向グラフ動的モード分解による河道網水位分布予測の検討”
〇⼤原由暉1, 茂⽊⼤知1, 村松正吾1, 早坂圭司1, 安⽥浩保1 (1. 新潟⼤学),“河川の流れの推定に対する物理的な制約を課した深層学習の適⽤性”


今回の発表を通じて,信号処理分野の専門家の方々から貴重なご意見を頂き,自身の研究内容を深める多くの気づきを得ることができました.また,様々な研究発表を聴講することで,新たな知識や刺激を得ることができ,研究への意欲が一層高まりました.これらの経験を糧に,さらなる研究成果の創出に向けて取り組んでいきたいです.

AuGFTのソースコード更新
Augmented Graph Fourier Transform (AuGFT) – File Exchange – MATLAB Central (mathworks.com) を更新しました。
新たにNumPy実装を追加しました。
TanSacNet Pre-release20250105 公開
接空間適応制御ネットワークの開発用に、TanSacNetプロジェクトを更新しました。
- 新しいPyTorch実装:PyTorchベースの2-D LSUNフレームワークを導入し、
orthonormalTransform.pyでのバッチ処理および低次元近似サンプルを含めました。PyTorchおよびCUDA環境での効率性を向上させるため、勾配計算と逐次行列処理を最適化しました。 - MATLABサポートの強化:MATLABワークフローの安定性とパフォーマンスを確保するため、データタイプとデバイス管理を改善しました。
- コードの改良と安定性:保守性を高めるためのコード構造の合理化と、両方のフレームワークにおける初期化とCPU処理の問題を改善しました。
このプレリリース版では、MATLABサポートの主な更新と全体的なコードの安定性とともに、新しいPyTorchの実装が反映されています。
APSIPA Transactions on Signal and Information Processing論文掲載
ITE Transactions on Media Technology and Applications論文掲載
以下の論文がITE Transactions on Media Technology and Applicationsに掲載されました。
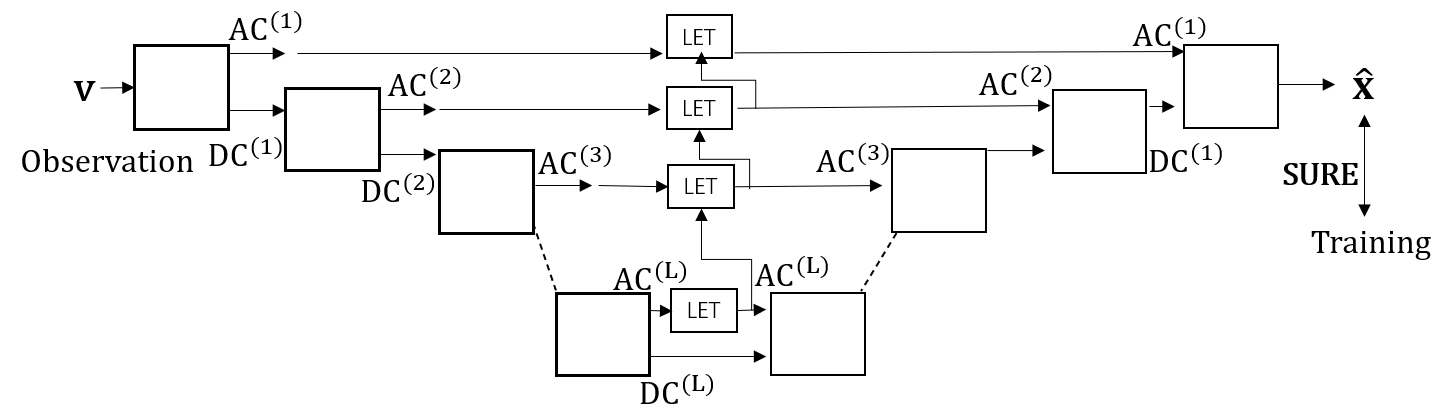
- Jikai Li, Shogo Muramatsu, [Paper] Structured Deep Image Prior for Image Denoising with Interscale SURE-LET, ITE Transactions on Media Technology and Applications, 2025, Volume 13, Issue 1, Pages 187-199, Released on J-STAGE January 01, 2025, Online ISSN 2186-7364, https://doi.org/10.3169/mta.13.187, https://www.jstage.jst.go.jp/article/mta/13/1/13_187/_article/-char/en,
- Abstract:
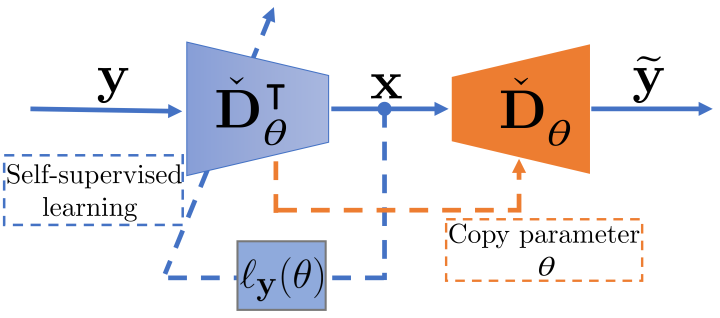
This study develops a self-supervised image denoising technique that incorporates a structured deep image prior (DIP) approach with Stein’s unbiased risk estimator and linear expansion of thresholding (SURE-LET). Leveraging interscale and interchannel dependencies of images to develop a multichannel denoising approach. The original DIP, introduced by Ulyanov et al. in 2018, requires a random image as the input for restoration, offering an advantage of not requesting training data. However, the interpretability of the role of the network is limited, and challenges exist in customizing its architecture to incorporate domain knowledge. This work integrates SURE-LET with Monte Carlo computation into the DIP framework, providing the reason of the random image supply and shifting the focus from generator to restorer design, thus enabling the network structure of DIP to more easily reflect domain knowledge. The significance of the developed method is confirmed through denoising simulations using the Kodak image dataset.